Artificial Intelligence is no longer just about chatbots or image generation. In real industries, AI is quietly doing something far more powerful — predicting the future.
Factories are predicting machine failures before breakdowns happen.
Energy plants are forecasting power demand hours and days in advance.
Manufacturers are predicting production output for upcoming shifts.
All of this is made possible by AI prediction models.
At TechKnowledge.in, we often receive questions like:
- Which AI model should I use for prediction?
- Can AI really predict machine faults?
- What’s the difference between energy prediction and production prediction models?
This article answers all those questions in simple, practical language, without heavy mathematics or marketing jargon.
What Are AI Prediction Models?
AI prediction models are machine learning systems trained on historical data to forecast future outcomes.
In simple words:
If you give AI enough past data, it can learn patterns and predict what is likely to happen next.
Examples:
- Predicting tomorrow’s energy consumption
- Predicting next shift production output
- Predicting machine failure before it happens
AI prediction models don’t guess randomly — they learn patterns from:
- Time
- Load
- Sensor data
- Environmental conditions
- Operating behavior
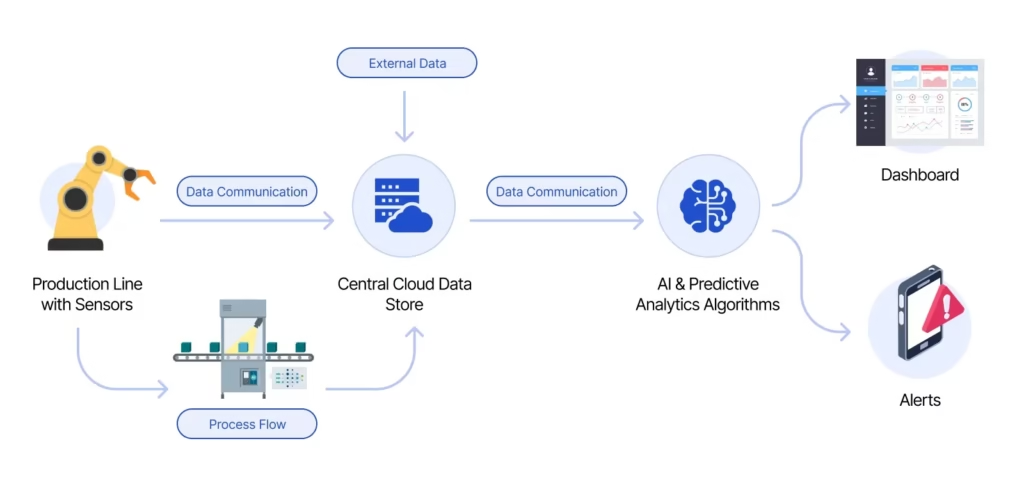
Where Are AI Prediction Models Used?
AI prediction models are already being used across industries:
- Manufacturing plants
- Energy & utilities
- Smart factories
- Oil & gas
- Logistics & supply chain
- Smart buildings
At TechKnowledge.in, we focus mainly on industrial and energy-related prediction use cases, because that’s where AI delivers maximum real-world value.
Types of AI Prediction Models (Explained Simply)
Let’s break down the most commonly used AI prediction models, along with where each one works best.
1. Linear Regression – The Foundation Model
Linear Regression is the most basic AI prediction model, but it is still widely used.
How it works
It finds a straight-line relationship between inputs and output.
Example:
Energy Consumption = Load × Factor + Constant
Where it is used
- Basic energy prediction
- Simple production forecasting
- Cost estimation
Pros
- Easy to understand
- Fast to implement
- Works with small datasets
Cons
- Cannot handle complex machine behavior
- Not suitable for vibration or fault prediction
Linear Regression is often the starting point when companies begin working with AI prediction models.
2. Decision Tree Models – Rule-Based Prediction
Decision Trees work like human decision-making.
Example:
If vibration is high AND temperature is rising → fault risk increases
Where it is used
- Fault classification
- Downtime analysis
- Quality issue prediction
Why industries like it
- Easy to explain to management
- Transparent logic
- Works with mixed data types
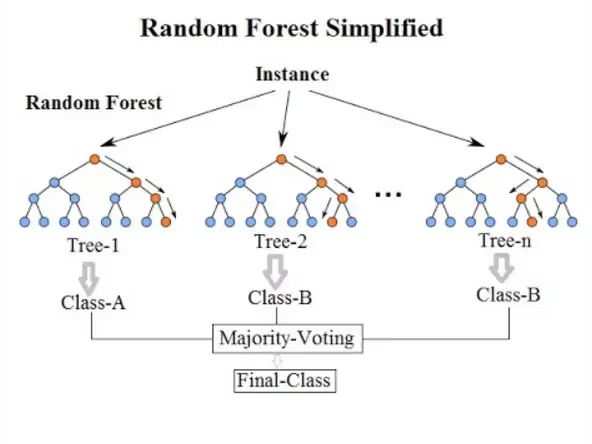
3. Random Forest – Multiple Decisions Combined
Random Forest is an advanced version of Decision Trees.
Instead of one tree, it creates hundreds of trees and combines their results.
Where it is used
- Production prediction
- Fault classification
- Energy consumption forecasting
Why it’s popular
- High accuracy
- Handles noisy industrial data well
- Less overfitting than single decision trees
At TechKnowledge.in, we often recommend Random Forest as a balanced AI prediction model for industrial use.
4. Gradient Boosting & XGBoost – High Accuracy Models
XGBoost is one of the most powerful AI prediction models used in industry today.
How it works
It builds models step by step, where each new model corrects the mistakes of the previous one.
Where it is used
- Energy demand forecasting
- Production output prediction
- Fault probability scoring
Why industries trust it
- Extremely accurate
- Works well with structured data
- Widely used in real production systems
For many energy and manufacturing projects, XGBoost becomes the final production model.
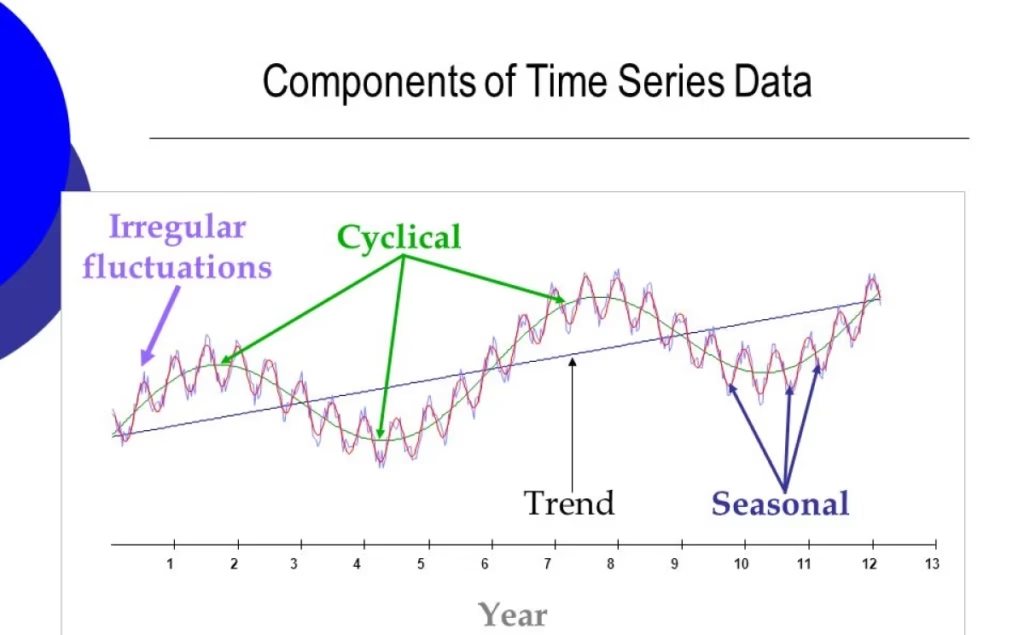
5. Time Series Models – Understanding Time Patterns
Time series prediction models focus on how values change over time.
Popular examples:
- ARIMA
- Prophet
Where they are used
- Hourly energy forecasting
- Daily production prediction
- Seasonal demand planning
Example
Predicting power consumption based on:
- Hour of the day
- Day of the week
- Season
6. Neural Networks & LSTM – Advanced AI Prediction Models
Neural Networks can learn very complex patterns.
LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) is a special neural network designed for time-series and sensor data.
Where they are used
- Predictive maintenance
- Vibration-based fault prediction
- Multi-sensor analysis
Why LSTM is special
- Remembers long-term trends
- Excellent for vibration, temperature, and current data
- Detects early fault patterns
Use Case 1: Energy Prediction Using AI Models
Energy prediction is one of the most common applications of AI prediction models.
Input Data
- Power load (kW)
- Time & shift
- Temperature
- Production activity
AI Models Used
- Linear Regression (basic)
- XGBoost (advanced)
- LSTM (real-time prediction)
Output
- Hourly energy forecast
- Peak load prediction
- Energy cost optimization
Energy prediction helps companies:
- Reduce electricity bills
- Avoid peak penalties
- Improve energy efficiency
Use Case 2: Production Prediction Using AI Models
Production prediction helps factories plan better.
Input Data
- Machine runtime
- Cycle time
- Downtime events
- Shift patterns
AI Models Used
- Random Forest
- Gradient Boosting
- Time series models
Output
- Shift-wise production forecast
- Monthly production planning
- Bottleneck identification
At TechKnowledge.in, we’ve seen production prediction improve planning accuracy by 20–30% in real factories.
Use Case 3: Fault Prediction – The Most Valuable Application
Fault prediction is where AI prediction models deliver maximum ROI.
Input Data
- Vibration RMS & FFT
- Temperature
- Motor current
- RPM (fixed or estimated)
AI Models Used
- Random Forest (fault type classification)
- XGBoost (fault probability)
- LSTM (early fault detection)
Output
- Fault type (bearing, misalignment, unbalance)
- Health score (0–100)
- Remaining useful life estimation
How to Choose the Right AI Prediction Model
| Application | Recommended Model |
|---|---|
| Energy Prediction | XGBoost / Prophet |
| Production Forecasting | Random Forest |
| Fault Detection | LSTM / XGBoost |
| Simple Systems | Linear Regression |
Common Mistakes People Make
- Choosing complex models with very little data
- Ignoring data quality
- Expecting 100% accuracy
- Not retraining models regularly
AI prediction models improve over time, not instantly.
Why AI Prediction Models Are the Future
AI prediction models are not replacing engineers — they are supporting decision-making.
They act like:
An experienced engineer who has seen thousands of machines and scenarios.
At TechKnowledge.in, we believe the future belongs to AI-assisted engineering, not blind automation.
Conclusion
AI prediction models are already transforming:
- Energy management
- Production planning
- Fault prevention
Understanding which model to use — and where — is more important than blindly applying AI.
This guide by TechKnowledge.in was written to help engineers, students, and decision-makers understand AI prediction models without confusion or hype.

